Das Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) ist zu einem integralen Bestandteil unseres täglichen Lebens geworden und ist in einer Vielzahl von Geräten wie Smartphones, Fernsehern, Computermonitoren und vielem mehr vorhanden. Als Verbraucher erwarten wir, dass diese Displays von dem Moment an einwandfrei funktionieren. Um jedoch die Zuverlässigkeit und Langlebigkeit von LCD-Displays zu gewährleisten, führen Hersteller einen wesentlichen Schritt durch, der als Alterungstest bekannt ist, bevor sie die Fabrik verlassen. Dieser Artikel soll die Gründe für die Notwendigkeit eines Alterungstests erklären, was es mit sich bringt, ob es dieLCD-Anzeigeund warum es immer noch Fälle geben kann, in denen Displays trotz des Bestehens des Alterungstests scheitern.
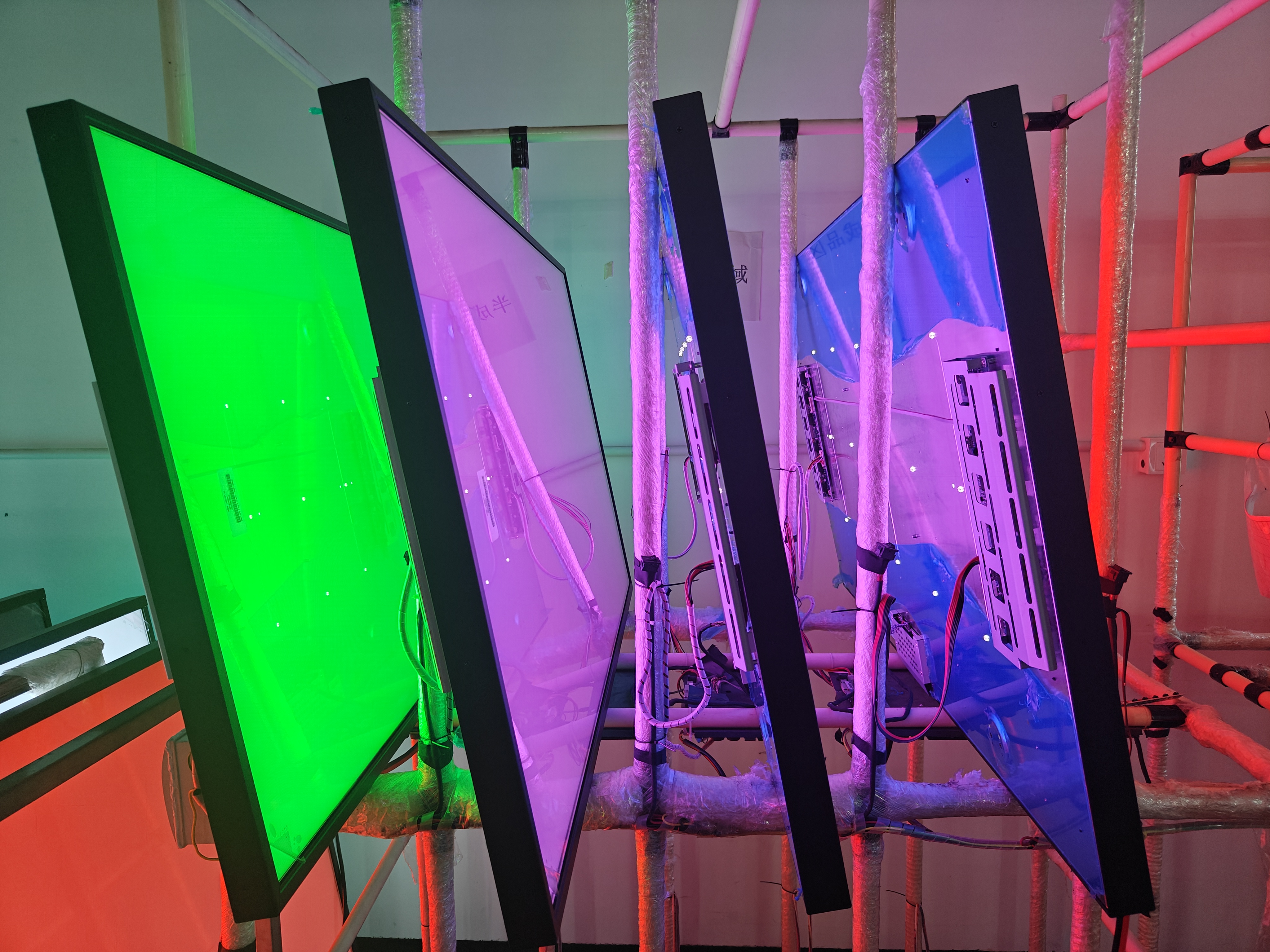

Gründe für die Durchführung eines Alterungstests:
1. Qualitätssicherung:
The primary reason for subjecting LCD displays to an aging test is to ensure quality assurance. These tests are performed to identify any potential defects, weaknesses, or malfunctions that may arise over time. By simulating the display's usage for an extended period, manufacturers can detect issues that might otherwise go unnoticed during initial inspection. This process helps in delivering a product that meets the highest standards of quality and reliability.
2. Stabilitätsbewertung:
LCD-Displays bestehen aus verschiedenen Komponenten, einschließlich der Flüssigkristalle, Hintergrundbeleuchtung, Polarisatoren und Steuerschaltungen. Jedes dieser Elemente kann von Faktoren wie Temperatur, Feuchtigkeit und Spannungsschwankungen beeinflusst werden. Ein Alterungstest ermöglicht es den Herstellern, die Stabilität dieser Komponenten unter verschiedenen Bedingungen zu beurteilen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie den Strengenheiten des realen Gebrauchs standhalten können. Es hilft bei der Identifizierung potenzieller Schwächen oder Schwachstellen, die dazu führen könnten, dass das Display vorzeitig ausfällt.
3. Leistungsbewertung:
Der Alterungstest dient auch als Mittel zur Bewertung der Leistung des LCD-Displays. Es ermöglicht es Herstellern, Parameter wie Farbgenauigkeit, Kontrastverhältnis, Helligkeitseinheit, Reaktionszeit und Betrachtungswinkel zu messen und zu analysieren. Indem die Anzeige längerer Nutzung ausgesetzt wird, können Hersteller ihre Fähigkeit einschätzen, im Laufe der Zeit eine konsistente Leistung aufrechtzuerhalten. Diese Bewertung hilft bei der Bereitstellung von Displays, die den Endnutzern ein optimales visuelles Erlebnis bieten.
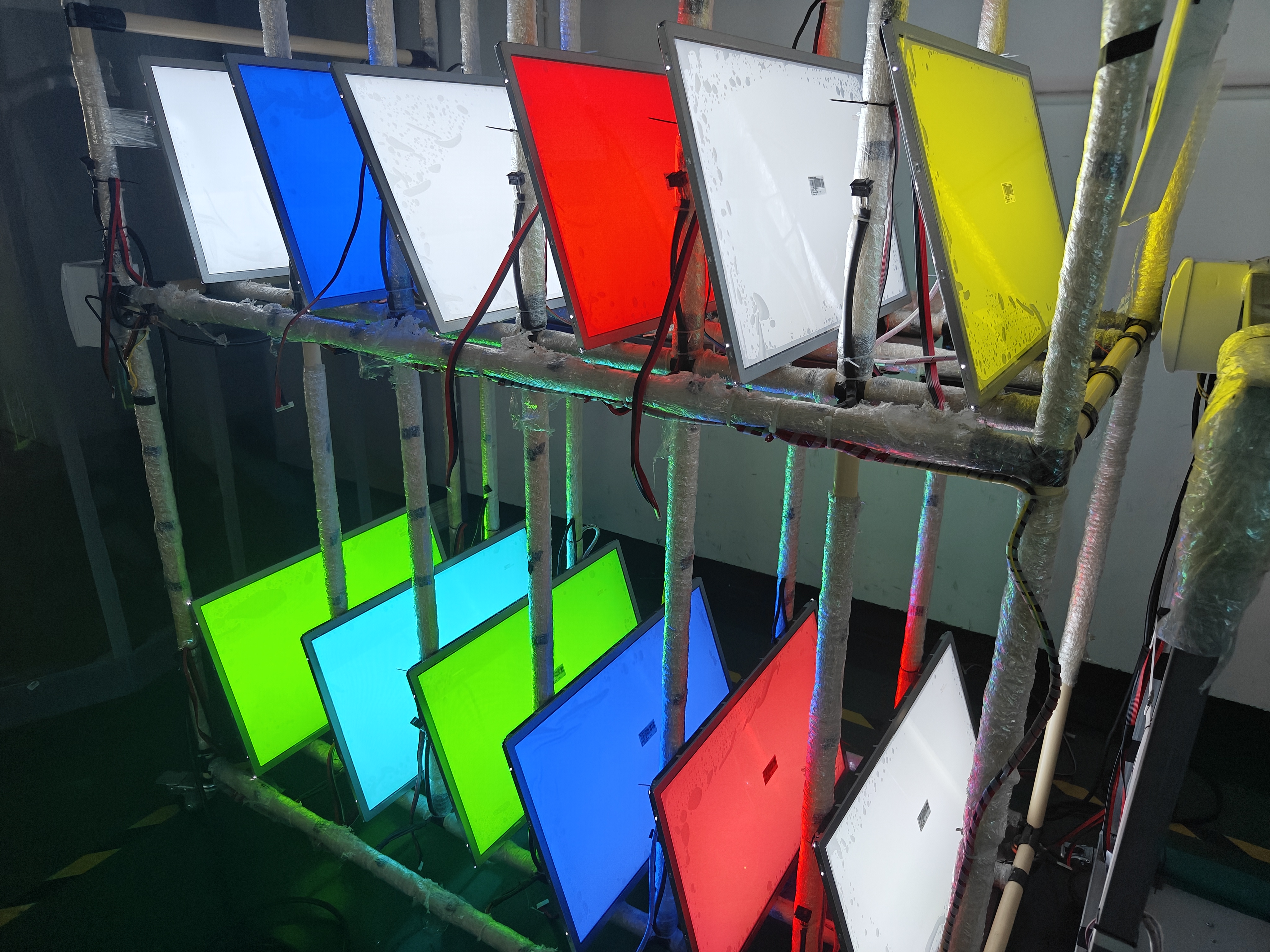

Alterungsprüfverfahren und seine Auswirkungen auf das LCD-Display:
The aging test typically involves subjecting the LCD display to continuous operation for an extended period, often ranging from several hours to several days. The display is connected to a test system that generates various patterns, colors, and images to simulate real-world usage scenarios. The test system monitors and records the display's performance parameters throughout the aging process.
Contrary to popular belief, the aging test itself does not damage the LCD display. The test is designed to mimic the normal usage conditions that the display will encounter during its lifespan. Manufacturers take precautions to ensure that the test environment, including temperature, humidity, and voltage levels, remains within safe limits. The purpose is to identify any potential issues that may arise during regular usage, not to cause damage.
The aging test primarily affects the display's backlight, which is responsible for illuminating the liquid crystals and producing the images we see. Backlights typically consist of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs). These light sources degrade over time, resulting in reduced brightness, color shifts, or even complete failure. By subjecting the backlight to continuous operation during the aging test, manufacturers can identify any potential backlight-related issues and ensure its longevity.
Despite Passing the Aging Test, Why Do Some Displays Fail?
While the aging test is a crucial step in ensuring the quality and reliability of LCD displays, there may still be cases where displays fail despite passing this test. Several factors can contribute to such failures:
1. Manufacturing Defects:
Although the aging test helps identify most manufacturing defects, it is not foolproof. Some defects may go undetected during the test due to their intermittent nature or the limitations of the test setup. These defects may manifest only after prolonged usage or under specific conditions, leading to display failures.
2. Handling and Transportation:
LCD displays are delicate and sensitive devices. Mishandling during transportation or improper installation can cause damage that may not be immediately apparent. While the aging test ensures the display's functionality before leaving the factory, external factors beyond the manufacturer's control can impact its performance during transit or installation.
3. Environmental Factors:
LCD displays are susceptible to environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to sunlight. Although the aging test simulates usage conditions, it cannot account for all possible environmental variations that the display might encounter once it reaches the end-user. Extreme temperatures, high humidity, or prolonged exposure to direct sunlight can degrade the performance and longevity of the display, leading to failures.
4. User Misuse or Negligence:
In some cases, displays may fail due to user misuse or negligence. Rough handling, improper cleaning methods, or exposure to liquids can damage the display, regardless of passing the aging test. It is essential for users to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for proper usage and maintenance to ensure the display's longevity.
Schlussfolgerung:
The aging test plays a vital role in ensuring the quality, reliability, and longevity of LCD displays. By subjecting the displays to extended usage under controlled conditions, manufacturers can identify potential defects, assess stability, and evaluate performance. Contrary to misconceptions, the aging test itself does not damage the displays. However, despite passing the aging test, there can still be cases where displays fail due to manufacturing defects, mishandling during transportation or installation, environmental factors, or user misuse. It is crucial for manufacturers and end-users to understand these factors and take necessary precautions to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of LCD displays.































